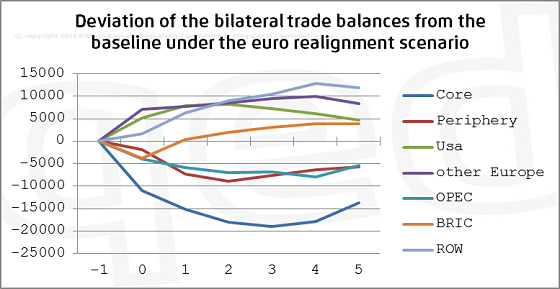
It is frequently claimed that the current EUR/USD exchange rate is too high and that a depreciation of the EUR against the USD would contribute to relieve the Eurozone economy from the current state of persistent crisis. Evidence provided by the a/simmetrie annual econometric model suggests that this claim is unsupported by the data, at least as far as the Italian economy is concerned. In fact, the size and sign of the trade elasticities show that the increases in net exports towards non-Eurozone countries, brought about by the depreciation of the euro, would be offset by an increase in net imports towards Eurozone countries, brought about by the increase in Italian domestic demand. To put it simply, in case of a depreciation of the EUR, the Italian economy would not only suffer a higher costs of energy (because of the depreciation vis-à-vis OPEC countries), but also spend in Germany much of the money it earned in the US, Japan, and the emerging countries, with a net effect likely to be almost zero or negative in the first three to four years.
F14 Empirical Studies of Trade
F17 Trade Forecasting and Simulation
F31 Foreign Exchange
F32 Current Account Adjustment
P51 Comparative Analysis of Economic Systems